Cisco 5548 Equivalent Netstat
Currently I have the following setup on a FAS - 3140.Head 1, single top level VIF that has 2 - 10gig interfaces (e4a, e4b). The main IP is 10.50.1.1 and a single alias of 10.50.1.2Head 2, single top level VIF that has 2 - 10gig interfaces (e4a, e4b).
The main IP is 10.50.1.3 and a single alias of 10.50.1.4These interfaces are plugged into a couple of Nexus 5548's, the VIF's are using LACP into the Nexus switches.Volumes are shared out via NFS to VMware servers.Our ESXi 4.1 servers have dual 10gig nics for storage, and they are setup with teaming in ESXi to use IP hash. Each of the hosts have a single IP on the same 10.50.1.x subnet, which is VLAN 50 for us.All of that works great.
I mounted the NFS volumes on ESX, by staggering the target IP's of the Filer Heads and I see almost equal traffic on and interfaces of the VIF's.Now we are migrating to Hyper V (dont ask) So I must move to iSCSI volumes/LUN's. I want to use MPIO on the Windows 2008 R2 hosts.I have read some NetApp docs and Microsoft docs that talk about using multiple subnets for host and target to make sure MPIO works properly. However I have seen setup (screen shots) that show all interfaces, using MPIO on the same subnet. In my current setup above we use the same subnet with NFS/VMware. So I am confused????Can I use my current configuration and just use the same subnet and then on my Windows 2008 R2 hosts just IP each of the two NIC's on the same subnet? Or should I do the following?Head 1, single top level VIF that has 2 - 10gig interfaces (e4a, e4b).
The main IP would be 10.50.1.1 and I would add an alias of 10.50.2.1?Head 1, single top level VIF that has 2 - 10gig interfaces (e4a, e4b). The main IP would be 10.50.1.2 and I would add an alias of 10.50.2.2?On the Windows 2008 R2 host I would then setup NIC 1 with 10.50.1.6 and NIC 2 with 10.50.2.6 pointing each NIC at a different Target IP when setting up the MS iSCSI initiator (with MPIO installed)??Would I still use LACP on the VIF's?Thanks for any help! Just use the same subnet and then on my Windows 2008 R2 hosts just IP each of the two NIC's on the same subnet?In this case all outgoing traffic will be sent via one interface only, according to routing table. This is simply how TCP/IP communication works. Not only it won't offer any load balancing (I really do not think it is an issue with 10G); the main problem is it may defeat any error recovery attempted by MPIO stack.In storage world established practice is to use two completely physically independent fabrics for conneciton; then storage stack on host provides full end-to-end error detection and recovery (and load balancing).Head 1, single top level VIF that has 2 - 10gig interfaces (e4a, e4b).
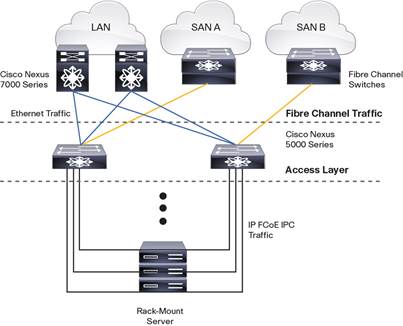
Cisco Nexus 5548
The main IP would be 10.50.1.1 and I would add an alias of 10.50.2.1?This means you will run two IP networks inside of single physical VLAN. Which now goes against networking best practices; and and has the same issue of defeating the main purpose of MPIO - to have several independent connections.But in your case (having single switch stack) it could be enough for load balancing purposes.
So you are saying neither of my proposed solutions will workSo I found these.andBoth of which are examples of having everything on the same subnet/vlan. Also I was reading another doc that walked through the MPIO setup with screen shots on the Windows side, it used the same subnet as well. It showed that when making the connections in the Microsoft iSCSI setup to choose Host IP 1 to Target IP 1 and on the second connection choose Host IP 2 to Target IP 2.example only had two NIC's on each side. My guess is that the MPIO software handles the communications, even with everything on the same subnet??It is all confusing at best. So you are saying neither of my proposed solutions will workNo, I'm just saying that I would prefer slightly different setupAlso I was reading another doc that walked through the MPIO setup with screen shots on the Windows side, it used the same subnet as well.Nobody is perfectMy guess is that the MPIO software handles the communications, even with everything on the same subnet?One point to note - source address selection is not equal to outgoing interface selection.
So it is perfectly valid to have session with source S1 going via interface with address S2. You cannot tell which route your packets take by looking on netstat (or similar) output.Good news is that on W2k8 it could actually work. I am not able to find relevant Microsoft documentation, but the article describes differences between weak and strong host models. In particular:If the source address has been specified, the source interface is known.
I need to create powershell equivalent of this command which will count no of conenctions established on port 80 and breakdown of ips. This woprked for me in Unix netstat -tnalp awk '$4 /:80/. Count no of established connections on port 80 and breakdown of each ip. The Netstat command equivalent on IOS 15. Ask Question 4. I have IOS Version 15.2(4)S4 on my router, and 'show control-plane host open-ports' does not work, is there any other command to generate such output? The 'show tcp brief' and 'show ip sockets' are not that good! How to configure Cisco remote access IPSEC VPN between IOS Router.
The source interface is assigned the source address.That said, you still have single point of failure - your LAN switch (stack). You still have single VLAN that handles all traffic. Any issues on this VLAN that disrupt traffic will affect both pathes in your MPIO setup. So as already mentioned, you will probably have load balancing but you will not actually have complete fault tolerance.That is not worse then it was with NFS. It is just that iSCSI allows to do better. Hi,Your challenge is a familiar one because of how the different protocols achieve redundance. NFSv3 can't do multiple networks, so Ethernet protocols are used to get redundancy.
ISCSI has Multi-pathing which offers both redundancy and increased bandwidth. With MPIO you need to have 2 subnets. Since you already have your 10GE links setup for Ethernet redundancy, you don't have enough nic's left to setup a sort of 'IP-SAN' connection redundancy where you might choose to have interfaces/vlans preferred to certain switches. Where vif's are not really necessary.The only good solution is to have another pair of 10GE interfaces, but barring that, just add a second vlan to get 2 iSCSI subnets (easier to move them later as vlans probably than stuffing 2 subnets into one vlan) and put your iscsi traffic there. You won't get traffic balanced perfectly but you get all of the advantages and perhaps a good basis to migrate things at a later date.
Netstat. 3 minutes to readIn this articleApplies To: Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8Displays active TCP connections, ports on which the computer is listening, Ethernet statistics, the IP routing table, IPv4 statistics (for the IP, ICMP, TCP, and UDP protocols), and IPv6 statistics (for the IPv6, ICMPv6, TCP over IPv6, and UDP over IPv6 protocols). Used without parameters, netstat displays active TCP connections. For examples of how this command can be used, see. Syntax Netstat -a -e -n -o -p -r -s ParametersParameterDescription-aDisplays all active TCP connections and the TCP and UDP ports on which the computer is listening.-eDisplays Ethernet statistics, such as the number of bytes and packets sent and received. This parameter can be combined with -s.-nDisplays active TCP connections, however, addresses and port numbers are expressed numerically and no attempt is made to determine names.-oDisplays active TCP connections and includes the process ID (PID) for each connection. You can find the application based on the PID on the Processes tab in Windows Task Manager.
This parameter can be combined with -a, -n, and -p.-p Shows connections for the protocol specified by Protocol. In this case, the Protocol can be tcp, udp, tcpv6, or udpv6. If this parameter is used with -s to display statistics by protocol, Protocol can be tcp, udp, icmp, ip, tcpv6, udpv6, icmpv6, or ipv6.-sDisplays statistics by protocol.
By default, statistics are shown for the TCP, UDP, ICMP, and IP protocols. If the IPv6 protocol is installed, statistics are shown for the TCP over IPv6, UDP over IPv6, ICMPv6, and IPv6 protocols. The -p parameter can be used to specify a set of protocols.-rDisplays the contents of the IP routing table. This is equivalent to the route print command.Redisplays the selected information every Interval seconds. Press CTRL+C to stop the redisplay. If this parameter is omitted, netstat prints the selected information only once./?Displays Help at the command prompt.Remarks.Parameters used with this command must be prefixed with a hyphen ( -) rather than a slash ( /).Netstat provides statistics for the following:.ProtoThe name of the protocol (TCP or UDP).Local AddressThe IP address of the local computer and the port number being used. The name of the local computer that corresponds to the IP address and the name of the port is shown unless the -n parameter is specified.
If the port is not yet established, the port number is shown as an asterisk (.).Foreign AddressThe IP address and port number of the remote computer to which the socket is connected. The names that corresponds to the IP address and the port are shown unless the -n parameter is specified. If the port is not yet established, the port number is shown as an asterisk (.).(state)Indicates the state of a TCP connection.