How To Tar A Directory
Sep 3, 2012 - If you want to tar the current directory, use. To designate that. On Linux, chances are your tar also supports BZip2 compression with the j. The Linux tar command is the swiss army knife of the Linux admin when it comes to archiving or distributing files. Gnu Tar archives can contain multiple files and directories, file permissions can be preserved and it supports multiple compression formats. The name tar stands for 'Tape Archiver', the format is an official POSIX standard.
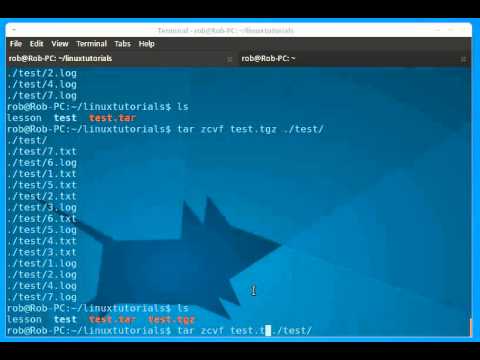
OverviewIn, the name of the tar command is short for tape archiving, the storing of entire file systems onto magnetic tape, which is one use for the command. However, a more common use for tar is to simply combine a few files into a single file, for easy storage and distribution.To combine multiple files and/or directories into a single file, use the following command: tar -cvf file.tar inputfile1 inputfile2Replace inputfile1 and inputfile2 with the files and/or directories you want to combine. You can use any name in place of file.tar, though you should keep the.tar extension. If you don't use the f option, tar assumes you really do want to create a tape archive instead of joining up a number of files. The v option tells tar to be verbose, which reports all files as they are added.To separate an archive created by tar into separate files, at the prompt, enter: tar -xvf file.tar. Compress and uncompress tar filesMany modern Unix systems, such as Linux, use GNU tar, a version of tar produced by the Free Software Foundation. If your system uses GNU tar, you can easily use gzip (the GNU file compression program) in conjunction with tar to create compressed archives.
To do this, enter: tar -cvzf file.tar.gz inputfile1 inputfile2Here, the z option tells tar to zip the archive as it is created. To unzip such a zipped tar file, enter: tar -xvzf file.tar.gzAlternatively, if your system does not use GNU tar, but nonetheless does have gzip, you can still create a compressed tar file, via the following command: tar -cvf - inputfile1 inputfile2 gzip file.tar.gz. If gzip isn't available on your system, use the Unix compress command instead. In the example above, replace gzip with compress and change the.gz extension to.Z (the compress command specifically looks for an uppercase Z). You can use other compression programs in this way as well. Just be sure to use the appropriate extension for the compressed file, so you can identify which program to use to decompress the file later.If you are not using GNU tar, to separate a tar archive that was compressed by gzip, enter: gunzip -c file.tar.gz tar -xvf -Similarly, to separate a tar archive compressed with the Unix compress command, replace gunzip with uncompress.Lastly, the extensions.tgz and.tar.gz are equivalent; they both signify a tar file zipped with gzip. Additional informationKeep the following in mind when using the tar command:.

How To Tar A Directory Structure
The order of the options sometimes matters. Some versions of tar require that the f option be immediately followed by a space and the name of the.tar file being created or extracted. Some versions require a single dash before the option string (for example, -cvf).GNU tar does not have either of these limitations.The tar command has many additional command options available.
For more information, consult the. At the shell prompt, enter: man tarGNU tar comes with additional documentation, including a tutorial, accessible through the GNU Info interface. You can access this documentation by entering: info tarWithin the Info interface, press? (the question mark) for a list of commands.